Did you know that 97% of websites remain inaccessible to people with disabilities, leaving billions of dollars in potential revenue untapped? Web accessibility benefits extend far beyond simply checking compliance boxes – they directly impact your bottom line.
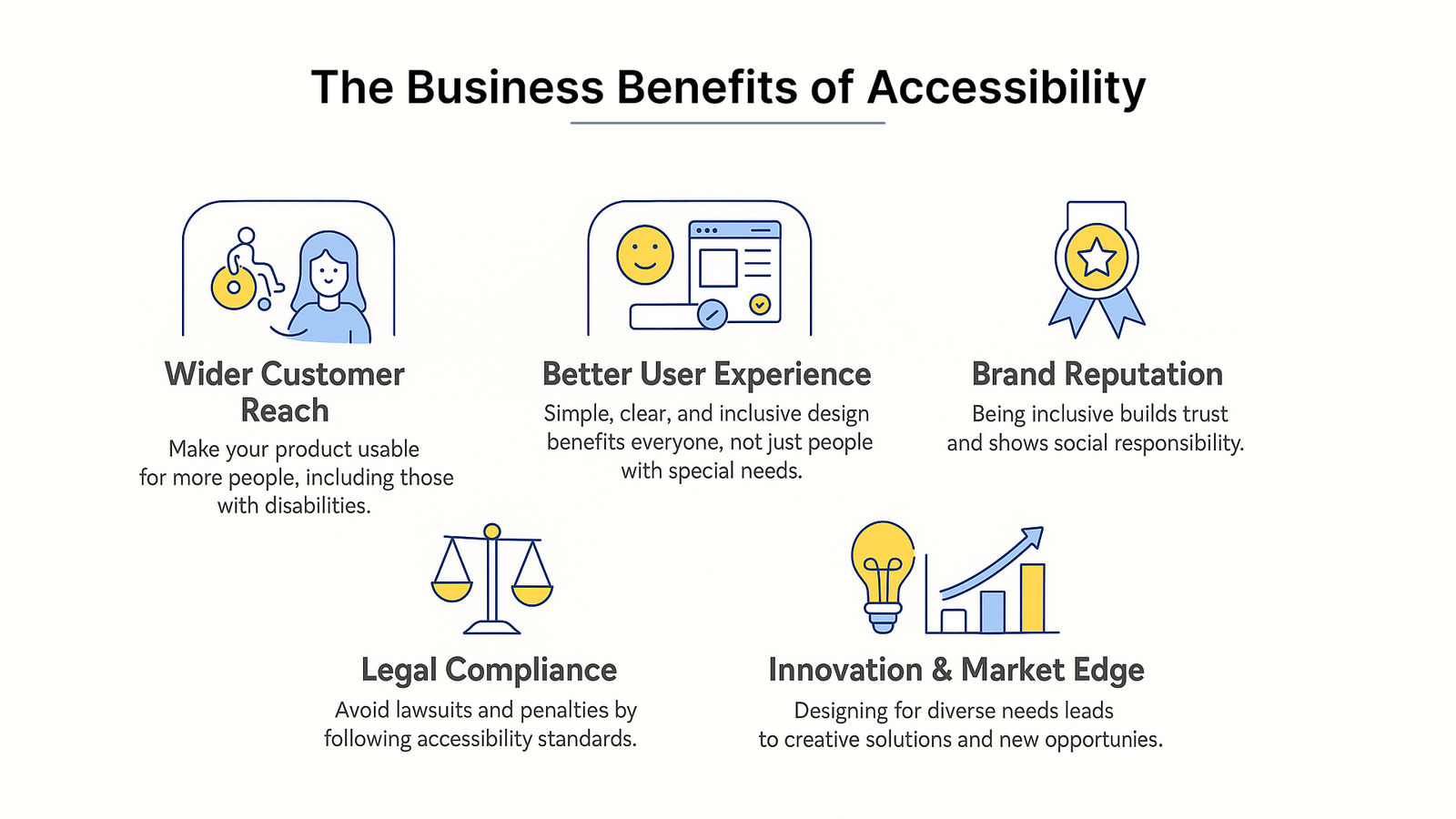
Despite the clear business opportunity, many companies overlook accessibility as merely a legal requirement. In fact, creating inclusive digital experiences opens your doors to a vast demographic with $8 trillion in annual disposable income. When we consider that people with disabilities and their families control over $13 trillion in spending power globally, accessibility becomes an obvious business priority.
Beyond avoiding potential lawsuits (which cost large companies an average of $100,000 each), accessibility delivers remarkable returns. Companies with strong accessibility programs see 28% higher revenue growth than competitors, and research shows every $1 invested in accessibility can yield up to $100 in benefits.
In this article, we’ll explore what web accessibility really means, why it’s important beyond compliance, and how implementing accessibility best practices creates lasting value through expanded market reach, improved user experience, and stronger customer loyalty.
What is web accessibility and why is it important?
Web accessibility represents much more than a technical standard—it’s about creating digital experiences that everyone can use, regardless of their abilities or circumstances. According to the Web Content Accessibility Initiative, web accessibility means designing websites, tools, and technologies so people with disabilities can perceive, understand, navigate, interact with, and contribute to the web.

Understanding digital accessibility
Digital accessibility encompasses making content usable for people with various disabilities, including visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, and neurological impairments. More specifically, it’s about removing barriers that prevent interaction with websites and digital content.
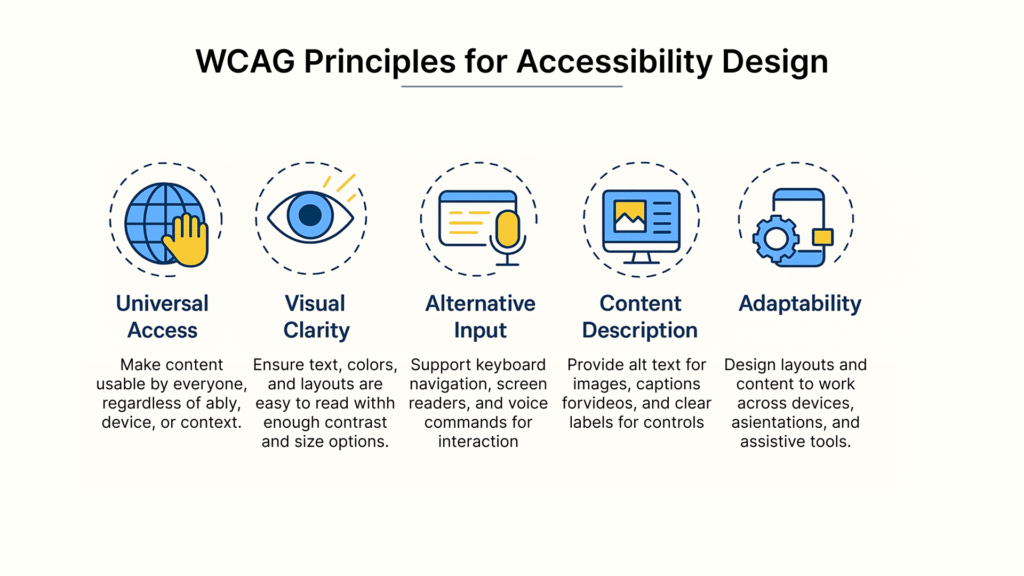
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide the framework for accessibility, organized under four essential principles:
- Perceivable: Information must be presentable to users in ways they can perceive regardless of sensory limitations
- Operable: Interface components must be navigable by all users
- Understandable: Information and operation must be comprehensible
- Robust: Content must be compatible with current and future technologies
Additionally, approximately 1.3 billion people—or one in six individuals worldwide—experience significant disability. Furthermore, a staggering 90% of websites remain inaccessible to people with disabilities who rely on assistive technology. These statistics highlight the substantial gap between digital accessibility needs and current implementation.
How accessibility impacts user experience?
Accessibility fundamentally enhances user experience for everyone, not just people with disabilities. For instance, captions originally designed for deaf users also benefit those watching videos in noisy environments or without sound. Similarly, high-contrast designs help people with visual impairments while simultaneously improving readability for users in bright sunlight.
Consequently, many accessibility features provide situational benefits. A study found that 71% of web users with disabilities will simply leave websites that aren’t accessible. At the same time, approximately one in four adults in the United States lives with some form of disability, representing a significant portion of potential users.
Beyond specific disabilities, accessibility supports users experiencing temporary limitations (like a broken arm) or situational constraints (such as holding a baby while using a device). Essentially, designing for accessibility often leads to solutions that improve experiences for all users.
Why compliance is not enough?
Although meeting accessibility standards is crucial, focusing solely on compliance misses the broader opportunity. A recent paper proposes shifting from compliance-centered accessibility to a care-driven model that prioritizes user autonomy. This approach acknowledges that accessibility isn’t about checking boxes but creating genuinely inclusive experiences.
Moreover, digital products that fully conform to WCAG 2.0 standards are expected to outperform market competitors by 50%. Nevertheless, an accessibility audit of Fortune 100 websites identified 815,600 WCAG accessibility issues, with most being basic Level A problems. This reveals how even major companies fail at fundamental accessibility requirements.
The legal landscape also continues to evolve, with digital accessibility lawsuits increasing by approximately 15% annually since 2018. However, the true value of accessibility extends far beyond avoiding litigation—it’s about creating emotional connections with users.
As one accessibility expert noted after working with clients with disabilities: “Accessibility shouldn’t just be about having equal access. It should also be about the experience of how you have access, and its emotional impact on you”. Therefore, the most effective approach treats accessibility not as a compliance exercise but as an integral part of creating excellent user experiences for everyone.
How accessibility expands your market reach?
Beyond ethical considerations, web accessibility benefits include tapping into a vast, often overlooked market segment. The digital accessibility landscape represents a substantial business opportunity that grows yearly as more organizations recognize its value.

The size and value of the disabled market
The numbers speak volumes about this market’s potential. Globally, approximately 1.3 billion people—roughly 16% of the world’s population or one in six individuals—live with some form of disability. In the United States alone, 28% of adults (about one in four) have a disability, with 12% facing mobility challenges, over 6% experiencing hearing difficulties, and nearly 5% having severe vision impairments.
What’s particularly compelling is the economic power this demographic wields. People with disabilities and their families control over INR 1096.95 trillion in disposable annual income. Even in specific sectors like travel, people with disabilities spend an average of INR 4455.29 billion yearly, demonstrating significant purchasing power across various industries.
Yet, a remarkable 90% of websites remain inaccessible to people who rely on assistive technology, creating a substantial gap between potential and realized market reach.
Tapping into underserved audiences
Given these figures, businesses that prioritize accessibility gain access to a considerably underserved market. First and foremost, the global digital accessibility software market was valued at USD 721.1 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1,300.3 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.2%.
Equally important, being digitally inclusive expands your customer base beyond those with permanent disabilities. As one research document explains, accessibility needs fall into three categories:
- Permanent disabilities: Long-term conditions affecting digital interaction
- Temporary impairments: Short-term circumstances like injuries
- Situational limitations: Environmental factors like forgetting glasses or holding a baby
By designing for these varied needs, your digital assets become usable in more contexts and situations, ultimately serving a broader audience.
Building inclusive digital experiences
Creating inclusive digital experiences yields tangible business benefits. Primarily, organizations that embrace inclusive design can tap into previously overlooked markets, reaching more potential customers and building stronger connections.
Indeed, this approach has become increasingly important to consumers. Roughly 59% of global consumers now consider inclusion an imperative when choosing brands, and 60% believe brands that fail to adopt inclusive designs will become “irrelevant”.
Besides this, accessible websites allow the entire disabled population—over 1.3 billion people—to explore your goods and services, potentially becoming customers. This inclusion opens new revenue streams and fosters brand loyalty and trust among diverse user groups.
The evidence is clear: accessibility isn’t merely about compliance—it’s a strategic business decision that expands your market reach, drives innovation, and creates lasting value through inclusive design.
The business benefits of accessibility
Investment in web accessibility delivers measurable business returns far beyond compliance considerations. A Forrester study found that every INR 84.38 invested in accessibility yields an impressive INR 8438.05 in returns, making it a sound business strategy worth implementing.
Improved SEO and discoverability
Web accessibility and search engine optimization share many technical requirements, creating natural synergy. Primarily, accessibility features like descriptive page titles, proper heading structures, and semantic HTML significantly improve how search engines crawl and index your site. Alt text for images—a critical accessibility feature—also helps search engines understand image content, potentially improving rankings in image search results.
Furthermore, well-structured content with proper headings doesn’t just help screen reader users navigate—it also helps search engines better understand your content hierarchy and relevance. Notably, accessible websites with proper metadata, including clear meta descriptions, enjoy higher click-through rates from search results pages, driving more qualified traffic to your site.
Higher conversion rates and lower bounce rates
Accessible websites consistently demonstrate superior performance metrics. Research shows that implementing accessibility best practices can increase conversions by up to 37%, directly impacting revenue. This occurs because accessible design creates clearer user journeys for everyone.
Data reveals that approximately 37% of consumers abandon e-commerce websites with poor navigation, while 42% decide within just 10 seconds whether to stay or leave a site. Through accessibility improvements like streamlined navigation and readable content, businesses experience:
- Lower bounce rates as more visitors can successfully use the site
- Longer average visit durations
- Higher engagement with key content and calls to action
One company reported that after implementing accessibility features, conversion rates nearly doubled year-over-year, demonstrating the substantial business impact of inclusive design.
Increased customer loyalty and retention
Accessible websites foster stronger connections with customers, driving loyalty and retention. Research indicates that companies prioritizing accessibility experience a remarkable 60% rise in repeat customers. This occurs because accessible sites signal brand values that resonate with consumers.
Survey data shows that 66% of consumers are willing to pay more for products from companies committed to positive social impact, while 92% are more likely to support companies that actively support individuals with disabilities.
Remarkably, businesses with strong accessibility practices report 30% higher Net Promoter Scores, indicating superior customer satisfaction. Additionally, customer referrals increase 2.5 times when accessibility is prioritized, expanding your customer base through positive word-of-mouth.
Beyond this, accessible design enhances overall user experiences, benefiting everyone regardless of ability. This universal improvement in usability creates positive associations with your brand, encouraging repeat visits and fostering lasting business relationships.
Reducing legal and operational risks
The financial implications of ignoring web accessibility extend far beyond missed market opportunities—they create substantial legal and operational risks that directly impact your bottom line.
Avoiding ADA and WCAG-related lawsuits
First and foremost, the cost of a single accessibility lawsuit can reach approximately INR 29,533,157.78, with settlements typically ranging from INR 421,902.25 to INR 1,687,609.02. In 2023 alone, federal ADA lawsuits exceeded 8,200, highlighting the growing legal risks. Organizations found non-compliant face initial fines often surpassing INR 6,328,533.81, with repeat violations potentially climbing to over INR 12,657,067.62.
Alongside these immediate expenses, non-compliance triggers additional costs:
- Legal fees and court expenses
- Potential public relations damage
- The expense of rebuilding your website to achieve compliance
The landscape is continuously evolving, with the Department of Justice releasing updated guidance in 2022 affirming that websites are indeed covered by the ADA as places of public accommodation.
Lowering support and maintenance costs
Interestingly, accessibility delivers operational savings beyond legal protection. According to a University of Twente case study, websites built with accessible design reduced ongoing maintenance costs by 66%. This occurs primarily because accessibility demands structure, resulting in cleaner code, consistent components, and thoughtfully designed interactions.
As a result, accessible websites experience fewer emergency fixes, reduced user complaints, and decreased technical debt. Clean, modular, well-documented accessible websites simply cost less to run.
Proactive vs reactive accessibility fixes
From a financial standpoint, fixing accessibility issues after development is substantially more expensive than addressing them upfront. Proactive accessibility means integrating these considerations from the project’s onset, eliminating the need for costly modifications later.
Subsequently, a mature accessibility program implements ongoing monitoring and regular audits, ensuring digital products remain compliant over time. This approach prevents the patchwork solutions that often result when accessibility is treated as an afterthought rather than a foundation.
Web accessibility best practices for long-term ROI
Implementing accessibility isn’t merely about avoiding risk—it’s about creating lasting value through strategic practices that boost long-term returns. To maximize your investment in accessibility, consider these proven approaches:
Start with an accessibility audit
An accessibility audit thoroughly evaluates your digital content against WCAG 2.2 guidelines and identifies usability barriers faced by people with disabilities. Comprehensive audits combine automated tools (which typically catch only 30-40% of issues) with essential manual testing. This process examines everything from headings and keyboard navigation to form fields and color contrast. Initially, focus on sampling key areas rather than every page: homepage, text-based content, multimedia elements, interactive features, login functionality, and navigation pages.
Integrate accessibility into design and development
Building accessibility from the ground up is significantly more cost-effective than retrofitting existing sites. Primarily, establish accessibility as a non-negotiable requirement in project briefs and kickoff meetings. Throughout development, implement proper heading structures, ensure form fields are correctly labeled, avoid purely visual instructions, and maintain sufficient color contrast. This approach creates cleaner code, consistent components, and thoughtfully designed interactions that reduce ongoing maintenance costs.
Use automation and assistive tools
Currently, several tools can streamline accessibility implementation:
- Automated testing tools: Options like ax DevTools, WAVE, and Accessibility Insights identify common issues
- Screen readers: JAWS, NVDA, and VoiceOver help test how content works for visually impaired users
- Alternative input devices: Head pointers, eye tracking systems, and specialized keyboards simulate different user experiences
Train teams and involve users with disabilities
Above all, accessibility requires involving actual users with disabilities throughout the development process. This reveals real-world issues that automated testing might miss. During evaluation, include users with various disabilities performing specific tasks on prototypes. Remember that input from one person with a disability doesn’t represent all people with disabilities—aim for diverse participation.
Conclusion
Accessibility truly extends far beyond checking compliance boxes or avoiding lawsuits. The evidence speaks for itself – organizations embracing accessibility experience 28% higher revenue growth, tap into a market of 1.3 billion people with significant purchasing power, and build stronger customer loyalty. Additionally, every dollar invested in accessibility can yield up to $100 in returns through expanded market reach, improved SEO, higher conversion rates, and reduced legal risks.
Rather than viewing accessibility as a technical burden, smart businesses recognize it as a strategic advantage. Accessible websites naturally align with search engine requirements, resulting in better rankings and increased discoverability. Users stay longer, engage more deeply, and convert at higher rates when navigating accessible interfaces.
Though 97% of websites remain inaccessible, this represents an enormous opportunity for forward-thinking companies. Starting with comprehensive audits, building accessibility into development processes, and involving actual users with disabilities creates digital experiences that welcome everyone.
Accessibility pays dividends through reduced maintenance costs, strengthened brand reputation, and protection from increasingly common ADA lawsuits. Most importantly, it connects your business with millions of potential customers who might otherwise be excluded from your digital experiences.
The business case for accessibility stands clear – it drives innovation, expands your audience, and delivers measurable returns. Accessibility isn’t just the right thing to do; it’s unquestionably the smart business decision that creates lasting value for everyone.
Key Takeaways
Web accessibility isn’t just about compliance—it’s a strategic business investment that drives revenue growth, expands market reach, and builds lasting customer relationships while reducing operational risks.
• Massive untapped market: 1.3 billion people with disabilities control over $13 trillion in global spending power, yet 97% of websites remain inaccessible to them.
• Strong financial returns: Every $1 invested in accessibility yields up to $100 in benefits, with accessible companies seeing 28% higher revenue growth than competitors.
• Improved performance metrics: Accessible websites experience up to 37% higher conversion rates, 60% more repeat customers, and significantly lower bounce rates.
• Legal and cost protection: Accessibility lawsuits can cost up to $100,000 each, while proactive accessibility reduces maintenance costs by 66% and prevents expensive retrofitting.
• SEO and discoverability boost: Accessibility features like proper headings, alt text, and semantic HTML naturally improve search engine rankings and click-through rates.
The key is integrating accessibility from the start rather than treating it as an afterthought. Companies that build inclusive digital experiences don’t just avoid legal risks—they create competitive advantages that drive sustainable growth and customer loyalty across all user segments.
FAQs
Q1. How does web accessibility benefit businesses beyond compliance?
Web accessibility expands market reach, increases revenue, and builds customer loyalty. It taps into a market of 1.3 billion people with disabilities, improves SEO, boosts conversion rates, and reduces legal risks. Companies prioritizing accessibility see 28% higher revenue growth and up to $100 in returns for every $1 invested.
Q2. What are the four main principles of web accessibility?
The four main principles of web accessibility are Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR). These principles ensure that digital content is accessible to users with various disabilities, making information perceivable, interfaces operable, content understandable, and technology compatible with current and future user tools.
Q3. How does accessibility impact user experience and customer loyalty?
Accessibility enhances user experience for everyone, not just those with disabilities. It leads to clearer navigation, better readability, and improved usability in various situations. As a result, accessible websites see up to 37% higher conversion rates, 60% more repeat customers, and significantly lower bounce rates, fostering stronger customer loyalty.
Q4. What are the financial implications of ignoring web accessibility?
Ignoring web accessibility can lead to substantial legal and operational risks. A single accessibility lawsuit can cost up to $100,000, with federal ADA lawsuits exceeding 8,200 in 2023 alone. Additionally, non-compliance can result in fines, legal fees, and damage to public relations. Conversely, proactive accessibility can reduce ongoing maintenance costs by 66%.
Q5. How can businesses implement accessibility best practices for long-term ROI?
To maximize ROI, businesses should start with a comprehensive accessibility audit, integrate accessibility into design and development processes from the beginning, use automation and assistive tools for testing, and involve users with disabilities throughout the development process. This approach creates cleaner code, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures digital products remain compliant over time.